Pay-per-click (PPC) marketing is a digital advertising model where your ad appears on search engines or social platforms and you only pay when someone clicks. With precise targeting, fast testing, and clear tracking, PPC is one of the quickest ways to drive qualified leads and sales.
Table of contents
1) What is PPC and how it works
Definition:
Pay-per-click (PPC) is an auction-based ad model. You choose keywords or audiences, write ads, set bids and budgets, and only pay when someone clicks.
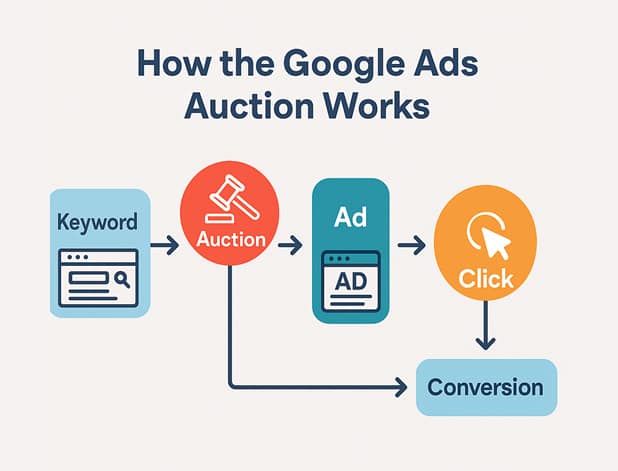
How the auction works in plain English:
- A user searches a keyword.
- Ads enter an instant auction based on bid + ad quality.
- Winning ads show in sponsored positions.
- You pay only when the user clicks, then your landing page does the selling.
Why brands use PPC:
Immediate visibility, tight targeting, full control of spend, measurable ROI.
2) PPC vs SEO
- PPC: instant traffic, scalable spend, great for testing offers and keywords.
- SEO: compounding organic visibility, slower to start, lower long-term cost per click.
- Best practice: use PPC to validate keywords and offers, then fold winners into SEO content and landing pages.
3) Where PPC ads run
- Search: Google Ads, Microsoft Advertising
- Shopping: Google Shopping, Microsoft Shopping
- Social: Meta, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok, X
- Display and Video: Google Display Network, YouTube
- Retargeting: across web and social to bring back non-converters.
Choose channels by goal:
- Lead gen B2B: Google Search + LinkedIn
- Ecom: Shopping + high-intent search + dynamic retargeting
- Local services: Google Search + Maps Local Services Ads + simple retargeting
4) How much does PPC cost
There is no single CPC. It varies by industry, competition, and quality.
Control your costs with:
-
- Tight match types and negatives to cut wasted queries
- Dayparting and geo targeting to focus on buyer windows and locations
- Quality Score improvements that lower CPCs over time
- Automated bidding with guardrails once conversion tracking is clean
5) KPIs that actually matter
- CPL or CPA: cost per lead or acquisition
- Conversion rate: landing page and form performance
- Qualified pipeline or revenue: the real north star
- Impression share and top-of-page rate: to diagnose lost opportunity
- Return on ad spend (ROAS) for ecom
Pro tip: report weekly on leading indicators (CTR, CVR, CPL) and monthly on lagging outcomes (pipeline, revenue).
6) Quality Score and Ad Relevance
-
Google rewards relevance with lower CPCs and better positions. Levers you can control:
- Keywords grouped by tight themes (single-theme ad groups)
- Ad copy that mirrors the keyword and the searcher’s intent
- Landing pages that keep the promise in the ad and load fast
- Ongoing query mining to add winners and block duds
7) Common PPC mistakes to avoid
- Broad, messy ad groups with mixed intent
- No negatives, so budget leaks into irrelevant clicks
- Sending all traffic to the homepage
- Tracking set up incorrectly or not at all
- “Set and forget” bidding with no testing plan
8) Step-by-step PPC setup checklist
Account and tracking
1. Install Google Tag and conversion events. Verify in real time.
2. Import offline conversions if you work leads through a CRM.
3. Set up custom conversions for phone calls and form submits.
Structure
4. Build campaigns by intent: Brand, Competitor, Non-brand High Intent, Retargeting.
5. Create tight ad groups with 3 to 5 close-variant keywords.
6. Write 8 to 12 responsive search ad headlines that echo the keyword and value prop.
7. Add all relevant ad assets: sitelinks, callouts, structured snippets, call extension.
Targeting and controls
8. Start with phrase/exact, layer negatives from day one.
9. Geo target realistically. Exclude regions that never convert.
10. Schedule ads during proven buyer hours, then test expansion.
Bidding and budgets
11. Launch with Maximize Conversions or tCPA once you have clean conversion data.
12. If new account, start with Enhanced CPC and switch to smart bidding after 30 to 50 conversions.
Landing pages
13. One page per intent with a single CTA, social proof, and fast load.
14. Track form events and scroll depth to diagnose friction.
Optimization cadence
15. Weekly: search term pruning, ad test rotation, bid checks.
16. Biweekly: add winners to exact, expand negatives, refresh creatives.
17. Monthly: restructure by performance, refresh offers, review attribution.
9) PPC FAQs
PPC means pay-per-click. You pay only when someone clicks your ad.
A digital ad model that places your message in front of high-intent users on search and social, and charges only on clicks.
Your ad enters an instant auction. Bid and quality determine position. You pay on click and convert on your landing page.
Yes if you track conversions, target intent, and keep testing. PPC is still the fastest channel to validate offers and generate pipeline.
Google for intent. LinkedIn for B2B targeting. Shopping for ecom. Retargeting everywhere.


